


Elevating knowledge: read our in-depth features

A new and ambitious startup called NUVIEW entered the geospatial satellite industry in May 2023, following a lengthy period in ‘stealth mode’. In this exclusive interview with GIM International, t...
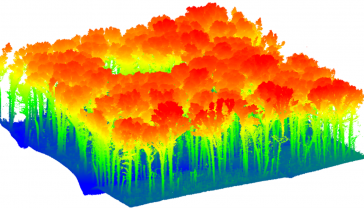
When considering Lidar technology for forest inventory, it is essential to evaluate the trade-offs of each platform. This article provides some pointers. There is a critical need for rapid, rigorous,...

Thanks to rapid improvements in aerial laser scanning systems, they offer great potential in road surveying compared with traditional photogrammetry-based methods. Using the high-density 3D point clou...

How can laser scanning and surveying firms stand out from the growing competition? This article provides tips for service providers striving to keep up with the latest technological trends while avoid...

A project in Aotearoa/New Zealand is combining the use of high-quality DEMs from satellite photogrammetric mapping (SPM) with Lidar technologies to model hazards such as snow avalanches. The resulting...

While it is possible to capture ancient Maya sites hidden beneath jungle canopy in remote locations using airborne Lidar, identifying them is still a time-consuming process. Typically, 3D point clouds...
The US Geological Survey (USGS) and Dewberry have jointly released a new topobathymetric Lidar dataset for the Potomac River, extending from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to the Chesapeake Ba...
ComNav has announced the launch of its latest innovation: the LS300 3D laser scanner. This addition to the company's product lineup signifies a significant leap forward in addressing the dynamic needs...
Driving new opportunities in the mapping landscape, a significant milestone has been achieved in New Zealand. With the introduction of 3D mapping data for the Waikato and Southland regions, access to ...
A new Lidar technique could help robotic vehicles avoid hazards when landing during future space missions to Mars or the Moon. The method uses flash Lidar to record full 3D images with a single laser ...
Lidar, short for Light Detection and Ranging surveying, represents a sophisticated measuring system leveraging the power of light. Widely recognized for its versatility, Lidar is extensively applied in diverse fields such as archaeology, forestry, geography, geology, seismology, remote sensing, and contour mapping. Its influence is steadily expanding into various geomatics applications, broadening its impact on different industries.
The market for laser scanning, a key component of Lidar technology, is experiencing robust growth. This surge is propelled by the development of more efficient and cost-effective methods for processing Lidar data. These advancements unlock new possibilities across a spectrum of disciplines, including but not limited to construction and engineering, industrial facilities, topographical applications, and cultural heritage preservation.
As Lidar continues to evolve, it plays a pivotal role in reshaping the landscape of measurement and mapping technologies. Its adoption is driven by the demand for higher precision and detailed data, fostering innovation and creating opportunities in fields where accuracy and spatial understanding are paramount. Whether unraveling the hidden features of archaeological sites or optimizing construction processes, Lidar stands as a transformative force in modern geospatial applications.
This site uses cookies. By continuing to use this website, you agree to our Cookies Policy. Agree